3D printing in manufacturing is one of those inventions that holds immense value over the traditional machining process and injection molding. In fact, in 2021, the 3D printing companies comprised about 0.1% of the global manufacturing market. The only catch is that with the promising nature of the technology, there are certain drawbacks to consider as well.
Since it is always a great practice, to know the ins and outs of your intended application, getting an idea of the pros and cons of 3D printing can be beneficial for you to decide whether it is worth it or not. Moreover, you will find an array of 3D printing technologies in the market, but most of the advantages and disadvantages are applicable to all of them.
Read on as the article breaks down a list of the positives and negatives of 3D printing in manufacturing along with understanding the essence of this technology.
Source: Industry today
How does 3D printing in manufacturing work?
3D printing in manufacturing utilizes a CAD or Computer-aided design for the creation of 3D objects, beginning from various materials such as powders and molten plastic. These printers are based on a layering method that builds the object your desire.
3D printing is a technology that goes hand in hand with additive manufacturing and utilizes similar techniques to that of a traditional inkjet printer but in 3D. This technology mixes up top-notch software, powdery materials clubbed with precision tools that together build a three-dimensional object from scratch.

What are the advantages of using 3D printing in manufacturing?
Let us quickly run through some of the pros in the use of 3D printing in manufacturing over traditional processes and why it could be a great step for your business and processes.
i). Speeding up
The biggest advantage of the setup of a 3D printer is that you can print most of the parts in less than a day and sometimes even produce components in less than an hour.
The main reason behind the fast process is the simple setup of the technology. While other technologies have a time-consuming setup, with 3D printers all you need to do is build preparation software.
In fact, about 55% of manufacturers felt that they experienced lower costs with the advent of 3D printing in their process. This is an added positive of using 3D printers in manufacturing processes.
ii). Designing freedom
3D printing in manufacturing also comes with the ability to create complex geometry. Moreover, there are many intricate designs that you just cannot make with the help of traditional methods largely because some of the areas will be impossible to make and cannot be removed from molds.
You can also simplify the design and replace the entire assembly with the help of one 3D-printed component.
iii). Demand-based printing
Your inventory can be taking up a lot of space, more so if the area is not being used right. If you aim to nullify the chances of an overstocked and expensive inventory, 3D printing gives you the chance to operate with a demand-based attitude.
To elaborate, this process utilizes just-in-time inventory management methods, and hence instead of bulk production, it frees up the inventory space along with the financial assets.
Additionally, 3D printing design files are housed in the CAD and STL file forms, which means you can maintain a virtual library of all these parts and print them when required and in the particular volume that suits you.
iv). Rapid prototyping and Iteration
Since the time required in the manufacturing process reduces significantly and there are far less stringent conditions, 3D printing gives you the ability to design rapidly. When you do that, the independence to improve the prototypes also increases.
On the contrary, most of the traditional methods will require a lot of time and a major investment, before you achieve a physical in-hand prototype. Using a 3D printer will allow you to get the part in just a week. Such a benefit allows engineers and designers to test and alter their ideas which eventually leads to rapid prototyping along with overall better designs.
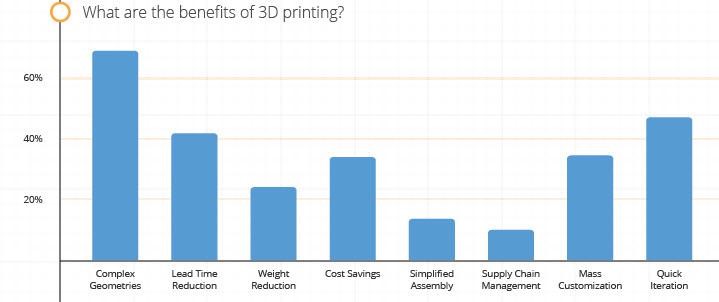
Source: Forbes
What are the disadvantages of 3D printing in manufacturing?
Despite the several pros of using 3D printing in manufacturing processes, you will not see it as an ideal fit in all situations. What matters here is the cost-benefit analysis i.e., comparing the pros and cons to see which outweighs the other. Here are some of the common cons of using 3D printing.
i). Uneven finish
If you are a fan of clean and consistent designs, 3D printing might not be the right fit for you. Since 3D printing in manufacturing takes place by building parts in a layer-by-layer fashion, you might see visible steps on these vertical surfaces. Such layer heights could play a strong role in other processes but if you were expecting something more visually pleasing, this might not cut it.
You can use post-processing technologies to better this issue such as vapor smoothing but you must know that you won’t be able to produce as good designs as that CNC machining or injection molding.
ii). Restricted build volume
You will find that most 3D printers like industrial-grade printers come with small build chambers when comparing them to mills and the injection mold process. If you are aiming to print a part larger than a build chamber of the printer, it should be divided into sections and then glued in a piece after processing.
The negative here is that this process is time taking, needs a lot of manual labor, and is expensive as well. All these cons together kill the purpose of using 3D printing in manufacturing in the first place.
iii). Part structure
Through the help of additive manufacturing, there are multiple parts printed in many layers which stick to each other during the process. But the issue arises when the design is put under stress or any sort of part orientation.
Since there are multiple layers clubbed together, they may separate which can even cause breakage of the part. You will find this issue more apparent in FDM when compared to other 3D printing technologies.
So, it is better to use injection molding if you want to prevent this delamination completely, especially for the parts under pressure.
iv). Fewer metal options
The metal options for 3D printing are much less than that of subtractive processes such as CNC machining. This can be negative if your project needs are better suited to metal options and processes.
Source: Cloudfront
FAQs
1). How does 3D printing affect manufacturing costs?
With 3D printing in manufacturing, you will cut the costs by a huge factor along with a reduction in the required storage space. The process enables them to make as and when they need to be sold which reduces any chances of overproduction and also helps with storage costs.
2). What is another name for 3D printing?
3D printing is also referred to as additive manufacturing– a process that allows you to make 3D solid objects from a digital file. This is because the creation of these parts is done via additive processes by laying down layers of material to ensure the right product is created.
3). Is 3D printing the future of manufacturing?
As of now, 3D printing as a concept has not taken over the manufacturing industry yet. However, analysts expect huge growth in the market of 3D printing in the years to come– beginning with USD 32.7 billion by 2023.
Conclusion
Industrial 3D printers have surely changed the way manufacturing processes used to take place and ensured that business owners get better products at lower expenses. 3D printing comes with numerous advantages that have ensured people opt for the technology.
But at the same time, there are certain negatives to the use of 3D printers, especially for some processes and parts. Overall, it is best to be aware of all the pros and cons before opting for this technology over other traditional methods.