“If you think the Internet has changed your life, think again. The IoT is about to change it all over again!” It seemed like yesterday when Aria Systems’ Brendan O’Brien made this claim, yet here we are, witnessing the massive revolution of the Internet of Things (IoT).
With the IoT, marketers have gone from “reach out to somebody” to “touch everything,” and manufacturers are empowering themselves to produce better-quality products that meet customer requirements.
As per Allied Market Research, the worldwide IoT in manufacturing market is projected to reach a massive $1,495 billion by 2030! This means the upcoming years will only see newer use cases for IoT in the manufacturing sector.
But as of 2022, what are the top 10 use cases for IoT in manufacturing? Let’s find out.
1). Supply Chain Management and Optimization
Source: Innovecs
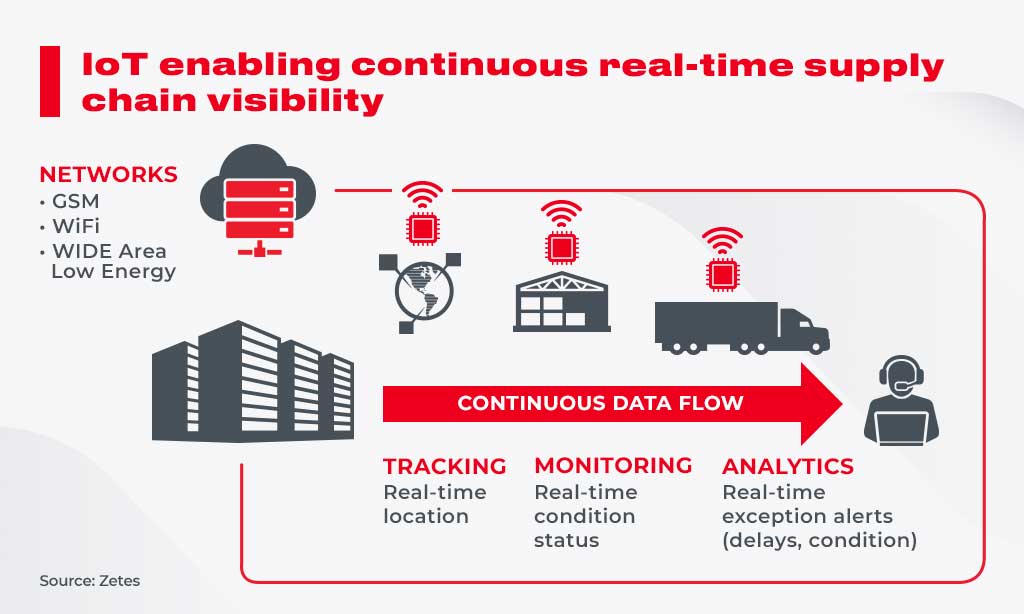
IoT in manufacturing has most definitely transformed supply chain management and optimization. It has made it easier for suppliers to track where goods are, where they are being stored, and when they can be expected at a specific location.
GPS and other related tools and sensors can authenticate and predict product locations. This way, customers can be given an exact date and time when they may receive their shipment.
Some of the main areas IoT covers in supply chain management and optimization include –
- Authentication of the exact location of goods by attaching sensors onto containers or the products themselves
- Tracking of traffic flow and speed of product movement to reduce handling time and improve efficiency
- Monitoring products in storage for the proper humidity, temperature, light intensity, etc. IoT devices may even sound an alarm in case a misbalance is detected.
- Contingent planning of alternative routes in case of delays in transit
- Easy identification of goods in storage by tagging them with IoT devices
- Quick and easy administration of goods upon receipt
This ultimately prevents goods from being delayed, lost in transit, or damaged. At the same time, customer satisfaction also improves.
2). Remote Monitoring
Source: Bridgera
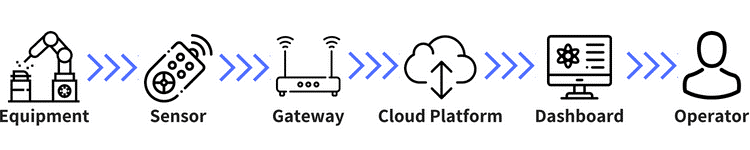
Based on the principle of ‘doing more with less,’ remote monitoring of products is a process that involves IoT sensors. These sensors monitor and gather data regarding machine operation and productivity, consequently delivering this information to an AI platform for analysis.
Personnel can access this information in real-time. They will have a finger on the pulse of the entire production line – from machine performance to any imminent breakdown. This is because remote monitoring via IoT can forecast breakdowns, so necessary steps could be taken to reduce downtime.
Here are some essential benefits that IoT in manufacturing offers through remote product monitoring:
- Cost reduction
- Reduction in downtime
- Machine uptime maximizes
- Accurate breakdown prediction
- It eliminates the need for intermediaries
- Reduced number of service calls
Let’s consider the example of Armal, a leading manufacturer of portable toilets. The company uses molding equipment to manufacture the components of its product. They wanted to monitor and optimize the equipment’s power consumption.
The next thing the company did was connect its IoT sensors to IoT industrial software. This way, they could track power consumption remotely through the entire production cycle.
3). KPI Compilation

Source: Adobe
A lot goes into play to understand whether the manufacturing process is functioning smoothly. This includes constant monitoring and analysis of performance metrics or Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). Dashboards, reports, etc., must be prepared and analyzed for understanding.
Thankfully, IoT in manufacturing is easing this process with real-time monitoring, detailed reports, and quick analysis. The system gives accurate insights into how the manufacturing process is running, areas needing improvement, etc.
This makes it easier to take necessary action to rectify the situation. Industrial IoT platforms use data collection and analysis to create simplified reports that condense lengthy results into easily digestible outcomes.
Some top benefits of this IoT use case in manufacturing include –
- Provides a solid basis for decision-making
- Increases efficiency in communication between departments
- It helps make better use of resources
- It saves time and money
- Improves worker safety
4). Automation
Source: Indiamart
Another area where IoT in manufacturing is being used heavily in developing industrial automation systems. No, this is not simply limited to a factory run by robots.
Though that can also be true, the use case is much deeper. For instance – what if someone accidentally presses the emergency button or the label printer suddenly runs out of paper? In such cases, the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) sensors will sound an alarm, sending a notification to the technician or operator’s smartwatch.
They can then take immediate action and save precious time and resources. Moreover, the industrial actions of UR+ robots (those that perform mundane, repetitive tasks) can be improved.
The top benefits of IoT in manufacturing automation include –
- Operational efficiency
- Strengthened access control
- Increased uptime
- Better customer insights
- Improved functionality
5). Predictive Maintenance
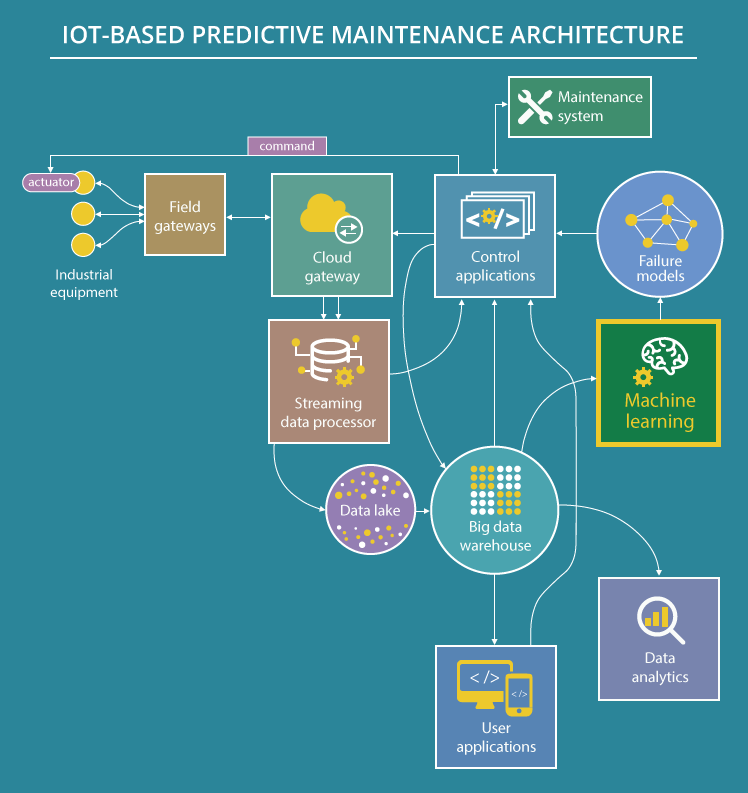
Source: Scnsoft
This process refers to predicting maintenance needs to avoid unnecessary downtime costs. Predictive maintenance considers three main areas – asset condition and performance, work order data, and MRO inventory usage.
The IoT tools and sensors collect information through the three areas, and the same is analyzed to make sense of areas that need immediate attention. Some examples of predictive maintenance include oil analysis, vibration analysis, equipment monitoring, thermal imaging, etc.
The main benefits of this process include –
- Minimization of downtime
- Reduction of hours that could be otherwise lost to maintenance
- Cost reduction
The Israeli food manufacturer, EcoPlant, uses predictive maintenance solutions. Their potato chip bags are sealed using nitrogen gas to keep the chips fresh for longer periods. Any inefficiency in air compression might contaminate the food while using up twice the allocated energy.
Through predictive maintenance, the company checks the functioning and performance of the air compression system’s valves, pipes, etc.
6). Quality Control

Source: Intuz
The process of quality control ensures the final product is free from any defects and meets customer expectations to the T. When done right, this process benefits both the manufacturer and customers. But, when gone wrong, it may harm profits and put customers at risk.
For instance – The Takata airbags disaster led to the biggest automotive recall. It involved almost 69 million airbag inflators with billions of dollars wasted. Such a recall can be avoided through effective quality control.
Here are the top benefits IoT in manufacturing provides when it comes to quality control –
- Easy detection of anomalies in the workflow
- Improvement in quality control models to adjust production quality to environmental changes
- Easy monitoring of inventory and storage conditions post-production
Let’s take the example of a company manufacturing sealed products such as a motherboard. It can be very challenging to inspect each component’s location and performance visually. In such cases, heat sensors can be used to see the positioning of each internal component before the green signal for product quality is given.
7). Worker Safety
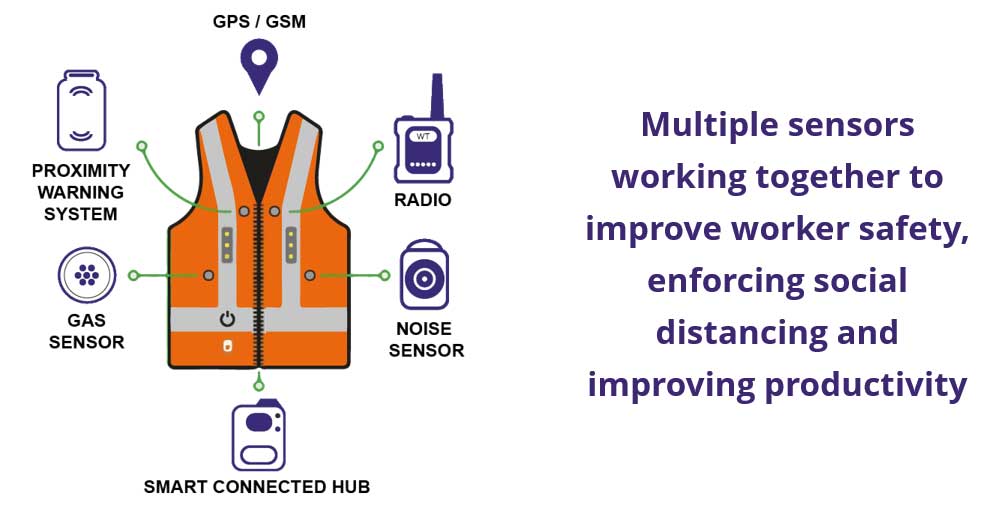
Source: Bell-Integration
Worker safety has not just been a concern but a top priority in every manufacturing factory. IoT in manufacturing can make work environments much safer. For instance – The air quality of the production plant can be drastically improved with the installation of HVAC sensors.
The Air Quality Index Software (AQ) will analyze the data received from the air sensors to ensure that the surrounding air quality is within the prescribed limits. Similarly, other hazards or injuries that threaten worker lives can be monitored and prevented.
From the viewpoint of worker safety, IoT in manufacturing offers the following benefits :
- Fire hazards can be prevented
- CO2 levels can be monitored
- Faster emergency response can be generated
- Workers can work stress-free, enjoying a greater sense of health and productivity
- Future incidents can be diagnosed and prevented
For example – FaceMe specializes in facial recognition technology, and the system can detect whether a worker is wearing their face mask properly. This helps in preventing the spread of COVID-19 among the workforce.
8). Digital Twins

Source: Dsidsc
For starters, digital twin technology helps make other processes more efficient, such as quality assurance and manufacturing. Digital twins are nothing but top-value replicas of physical systems, devices, places, etc.
These twins offer dual benefits to data specialists. They enable the real-time monitoring of an extant object and help stimulate an object. Digital twin IoT in manufacturing can enhance supply chain visibility.
For instance – asset trackers can be attached to containers to monitor the real-time location of goods and environmental conditions. Once the data has been transferred to a digital twin, the same can be used by the business owner to track the movement of goods along the supply chain.
This digital twin can be used for other purposes such as monitoring air quality, foot traffic, lighting, etc. Still, the top benefits of digital twins include :
- Easy risk assessment
- Predictive maintenance
- Better team training and collaboration
- Better financial decision-making
- Real-time remote monitoring
9). Fleet Management
Source: Fleetroot
With last-mile delivery and reverse logistics solutions coming in, customer expectations are higher than ever. Manufacturers have slim chances of overcoming the loss of goods-in-transit or time. As such, GPS trackers can be implanted onto buses and other logistics vehicles to facilitate real-time monitoring of goods.
This data can be analyzed by fleet management software to calculate how long the transit will take. This will help production and inventory managers to stay prepared. Also, if a vehicle breaks down along the way, a notification will be sent for it to be towed to a nearby service station.
This function of IoT in manufacturing is perhaps the most important one of all. As such, top benefits include –
- More optimized maintenance and logistics
- Easy monitoring of driver performance for the safety
- Better fuel efficiency
- Better compliance with safety and environmental regulations
- Reduced costs and risks involved
10). Workforce Efficiency

Source: PTC
This has to be the final point we discuss, as the culmination of the nine mentioned above would result in a more productive workforce. With all the mundane, repetitive, and time-consuming tasks out of the way, workers should have sufficient time to fulfill their advanced core duties.
Additionally, wearable tech such as a smartwatch allows data between machines and personnel to be exchanged easily. So, if there is an assembly line breakdown, the smartwatch can automatically notify the personnel.
As a result, maintenance staff can immediately get to repair work. Similarly, when a fresh batch of goods arrives, the fleet management software can automatically alert the personnel via the smartwatch, and preparations can be made accordingly.
So, IoT in manufacturing ultimately leads to worker productivity, minimized wastage of time and resources, and reduced risk.
Parting Thoughts
Though IoT in manufacturing has a vast scope, it is equally valid that there are still challenges to overcome. These include – significant investments, robust infrastructure, solid data security, well-trained employees, and integration with older systems.
However, given the many possibilities, the challenges shall be overcome as we see the future of manufacturing built upon the firm foundation of connected devices. If there’s one certain thing, it’s this – IoT devices will gradually eliminate most to all of the manual activities in the manufacturing sector!
Most Common FAQs
1. What are some top IIoT Hurdles Yet to Overcome?
Despite the rapid adoption of IIoT industry-wide, there are still challenges to overcome, such as security threats, making sense of siloed data, and striking a balance between operational technology and information. These, in turn, may adversely impact the ROI.
2. What does the Future of IoT in Manufacturing Hold?
Notwithstanding the challenges, the future of IoT in manufacturing is bright. Some top upcoming trends we may observe are greater adoption of predictive maintenance, enhanced cybersecurity in plants, and process optimization via integrated technologies.